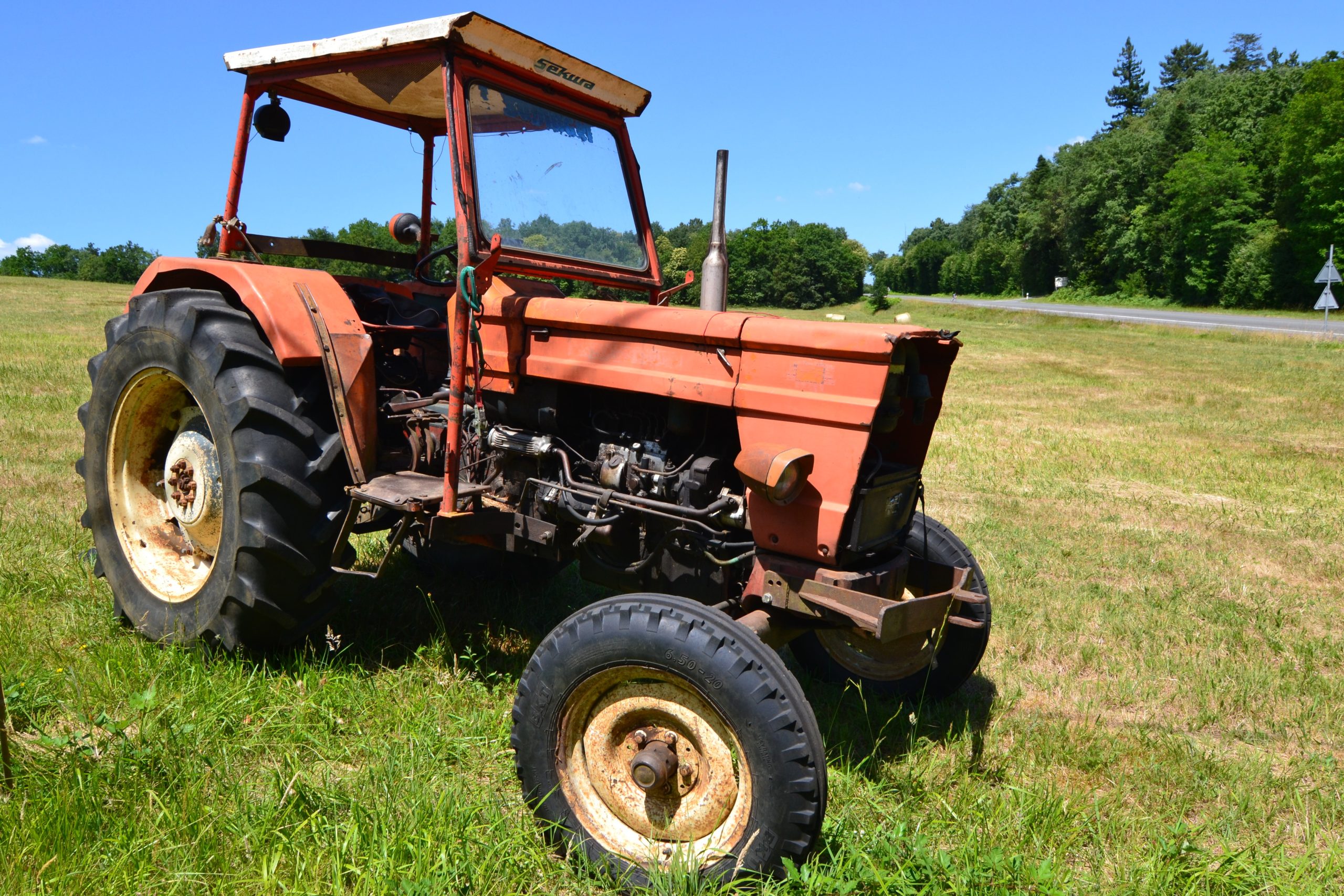
 When an item is repaired, it is reasonable to expect it to be safe and free of defects upon its return. However, when an injury occurs after a product’s repair, the injured party is entitled to seek damages. For example, Joe McPherson suffered a knee injury after the battery compartment of a tractor, which Ronald Dauzat repaired, fell apart. The question of negligence and responsibility arose, leading to a legal dispute and subsequent appeal.
When an item is repaired, it is reasonable to expect it to be safe and free of defects upon its return. However, when an injury occurs after a product’s repair, the injured party is entitled to seek damages. For example, Joe McPherson suffered a knee injury after the battery compartment of a tractor, which Ronald Dauzat repaired, fell apart. The question of negligence and responsibility arose, leading to a legal dispute and subsequent appeal.
Dauzat sold his old tractor to McPherson. However, it did not function properly, so Dauzat took it in for repairs. Dauzat notified McPherson the tractor was ready to be picked up. When McPherson arrived at the shop, Dauzat was not there. But two men he assumed were employees permitted him to mount and inspect the tractor. When McPherson tried to demount, the battery compartment fell apart, and he fell and wounded his knee
McPherson filed a lawsuit against Dauzat for his injury. His complaint alleged the defective tractor caused his injuries. He stated that his injury would have been prevented if the battery box had been firmly latched. Dauzat filed an involuntary dismissal and claimed McPherson failed to present evidence that the unlatched box was the cause of his fall.
 Insurance Dispute Lawyer Blog
Insurance Dispute Lawyer Blog
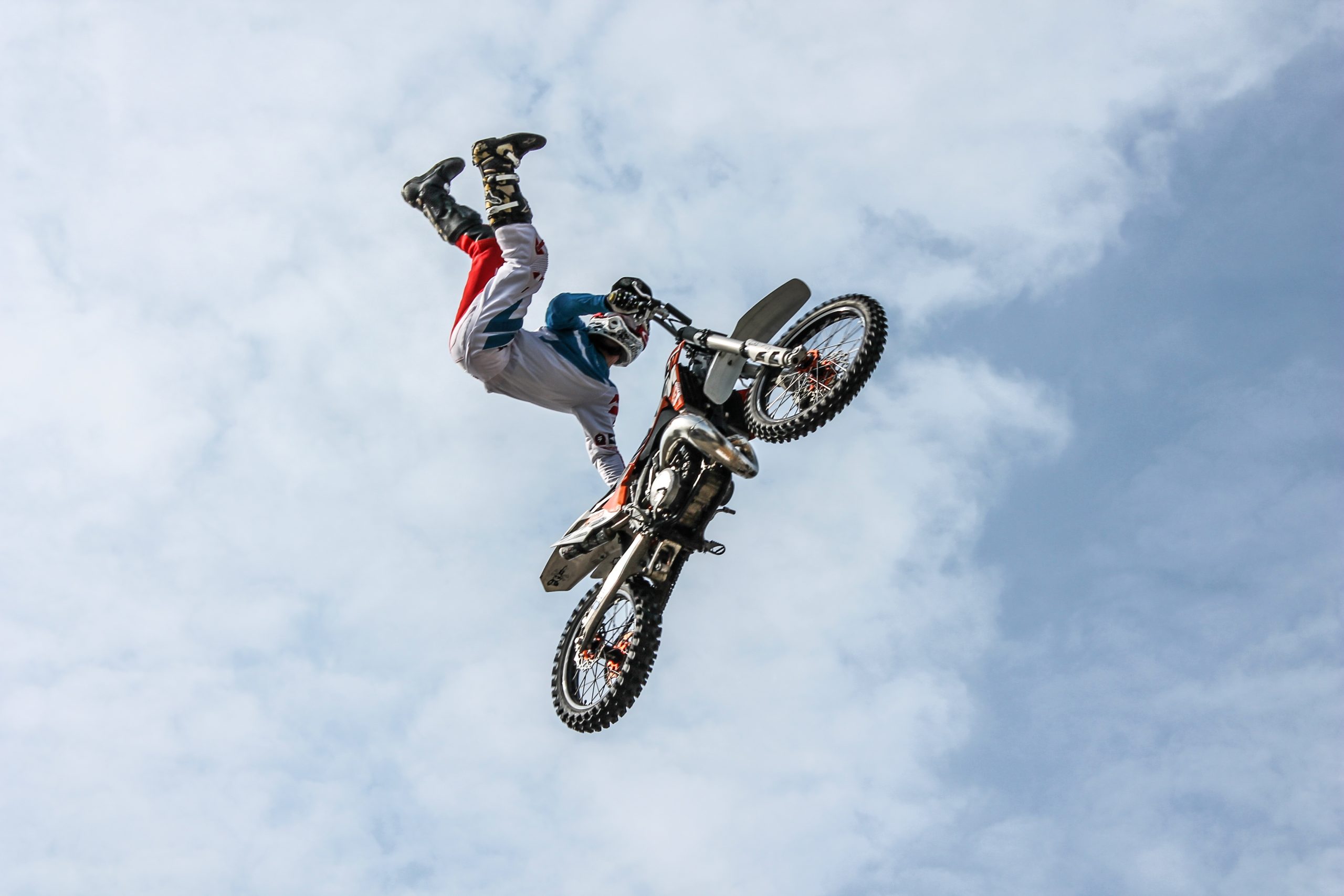

 Even if you have a unique job like a stunt performer, you can still get brought down to Earth by the complexities of determining what your insurance policies do and do not cover if you are involved in an insurance coverage dispute. In that case, it is important to understand the plain language of your insurance contract, how different provisions in the policy interact, and how courts interpret insurance policies.
Even if you have a unique job like a stunt performer, you can still get brought down to Earth by the complexities of determining what your insurance policies do and do not cover if you are involved in an insurance coverage dispute. In that case, it is important to understand the plain language of your insurance contract, how different provisions in the policy interact, and how courts interpret insurance policies.  Navigating bureaucracy and red tape is a common experience when dealing with government agencies and trying to obtain workers’ compensation benefits. However, if you find yourself frustrated by what seems like an improper requirement, you might be able to challenge an administrative agency’s actions as exceeding its authority, as Calvin Arrant did here.
Navigating bureaucracy and red tape is a common experience when dealing with government agencies and trying to obtain workers’ compensation benefits. However, if you find yourself frustrated by what seems like an improper requirement, you might be able to challenge an administrative agency’s actions as exceeding its authority, as Calvin Arrant did here.  Personal injury cases are notorious for their intricate nature, often posing challenges in determining fault and establishing liability. Complications escalate further when discrepancies arise regarding the facts surrounding the incident. When blame is uncertain, and parties refuse to accept responsibility, the legal landscape becomes increasingly convoluted.
Personal injury cases are notorious for their intricate nature, often posing challenges in determining fault and establishing liability. Complications escalate further when discrepancies arise regarding the facts surrounding the incident. When blame is uncertain, and parties refuse to accept responsibility, the legal landscape becomes increasingly convoluted.  Filing a claim in court requires careful consideration of the appropriate time frame, as it can significantly impact the success of a lawsuit. This is particularly crucial when dealing with actions such as false arrest and false imprisonment, where prescription periods play a significant role.
Filing a claim in court requires careful consideration of the appropriate time frame, as it can significantly impact the success of a lawsuit. This is particularly crucial when dealing with actions such as false arrest and false imprisonment, where prescription periods play a significant role.  In some cases, mistakes in following procedure can harm a plaintiff’s cause of action even if the case otherwise may be successful on the merits. For example, legal malpractice cases in Louisiana must be filed within one year from when the plaintiff knew or should have known that malpractice had occurred. A recent case out of the Parish of East Baton Rouge has outlined when a plaintiff is considered to have some notice of legal malpractice.
In some cases, mistakes in following procedure can harm a plaintiff’s cause of action even if the case otherwise may be successful on the merits. For example, legal malpractice cases in Louisiana must be filed within one year from when the plaintiff knew or should have known that malpractice had occurred. A recent case out of the Parish of East Baton Rouge has outlined when a plaintiff is considered to have some notice of legal malpractice.  Although you may be excited if you are awarded damages at trial, your award might still face a challenge on appeal. Therefore, when you are involved in a trial for an accident in which you were harmed, it is important to understand what evidence you need to present so that any money you are awarded can survive a challenge on appeal.
Although you may be excited if you are awarded damages at trial, your award might still face a challenge on appeal. Therefore, when you are involved in a trial for an accident in which you were harmed, it is important to understand what evidence you need to present so that any money you are awarded can survive a challenge on appeal.  Simple driving accidents happen every day due to lapses in inattention. The results of these lapses can have devastating consequences. Whose is at fault in an accident when both parties were less than perfect in assessments of dangers on the road? The subsequent lawsuit from Louisiana shows how a court will determine how much fault each party bears for an accident and adjust damages based on that outcome.
Simple driving accidents happen every day due to lapses in inattention. The results of these lapses can have devastating consequences. Whose is at fault in an accident when both parties were less than perfect in assessments of dangers on the road? The subsequent lawsuit from Louisiana shows how a court will determine how much fault each party bears for an accident and adjust damages based on that outcome. An employee injured at work while performing the functions of her job is generally entitled to worker’s compensation. But what about a worker injured on the job by the intentional act of a fellow employee? An action for recovery due to employer negligence could be a better option.
An employee injured at work while performing the functions of her job is generally entitled to worker’s compensation. But what about a worker injured on the job by the intentional act of a fellow employee? An action for recovery due to employer negligence could be a better option. Allocating damages in a wrongful death case is challenging because putting a price on a life is hard. Therefore, if a family in a wrongful death case feels the jury abused its discretion in calculating that monetary value, then the family can resort to a motion for JNOV to try and correct the decision. However, this is a rigorous standard, and a recent case out of Baton Rouge outlines how a court reviews these motions.
Allocating damages in a wrongful death case is challenging because putting a price on a life is hard. Therefore, if a family in a wrongful death case feels the jury abused its discretion in calculating that monetary value, then the family can resort to a motion for JNOV to try and correct the decision. However, this is a rigorous standard, and a recent case out of Baton Rouge outlines how a court reviews these motions.